数据处理(numpy & pandas & scipy & matplotlib.pyplot)
numpy
参考网址: https://www.jianshu.com/p/57e3c0a92f3a 啥都解释了:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/20878530
小知识点
- 迭代对象与迭代器:https://blog.csdn.net/jinixin/article/details/72232604 my_list_iter = iter(my_list) # 得到该对象的迭代器实例,iter函数在下面会详细解释(iter获取迭代器。。。)
- 生成器是一种特殊的迭代器,生成器自动实现了“迭代器协议”(即__iter__和 next方法),不需要再手动实现两方法。
- 生成器在迭代的过程中可以改变当前迭代值,而修改普通迭代器的当前迭代值往往会发生异常,影响程序的执行。
#数学之美
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def mandelbrot(h, w, maxit=20):
y, x = np.ogrid[-1.4:1.4:h * 1j, -2:0.8:w * 1j]
c = x + y * 1j
z = c
divtime = maxit + np.zeros(z.shape, dtype=int)
for i in range(maxit):
z = z ** 2 + c
diverge = z * np.conj(z) > 2 ** 2 # who is diverging
div_now = diverge & (divtime == maxit) # who is diverging now
divtime[div_now] = i # note when
z[diverge] = 2 # avoid diverging too much
return divtime
plt.imshow(mandelbrot(400, 400))
plt.show()

柱形图 hist
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Build a vector of 10000 normal deviates with variance 0.5^2 and mean 2
mu, sigma = 2, 0.5
v = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, 10000)
# Plot a normalized histogram with 50 bins
plt.hist(v, bins=50, normed=1) # matplotlib version (plot)
plt.show()
柱形图的顶点线型图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Build a vector of 10000 normal deviates with variance 0.5^2 and mean 2
mu, sigma = 2, 0.5
v = np.random.normal(mu, sigma, 10000)
# Compute the histogram with numpy and then plot it
(n, bins) = np.histogram(v, bins=50, normed=True) # NumPy version (no plot)
plt.plot(.5 * (bins[1:] + bins[:-1]), n)
plt.show()
合并:https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/data-manipulation/np-pd/2-6-np-concat/
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A' : 1.,
'B' : pd.Timestamp('20130102'),
'C' : pd.Series(1,index=list(range(4)),dtype='float32'),
'D' : np.array([3] * 4,dtype='int32'),
'E' : pd.Categorical(["test","train","test","train"]),
'F' : 'foo'})
print(df2)
"""
A B C D E F
0 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
1 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
2 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 test foo
3 1.0 2013-01-02 1.0 3 train foo
"""
数据清洗
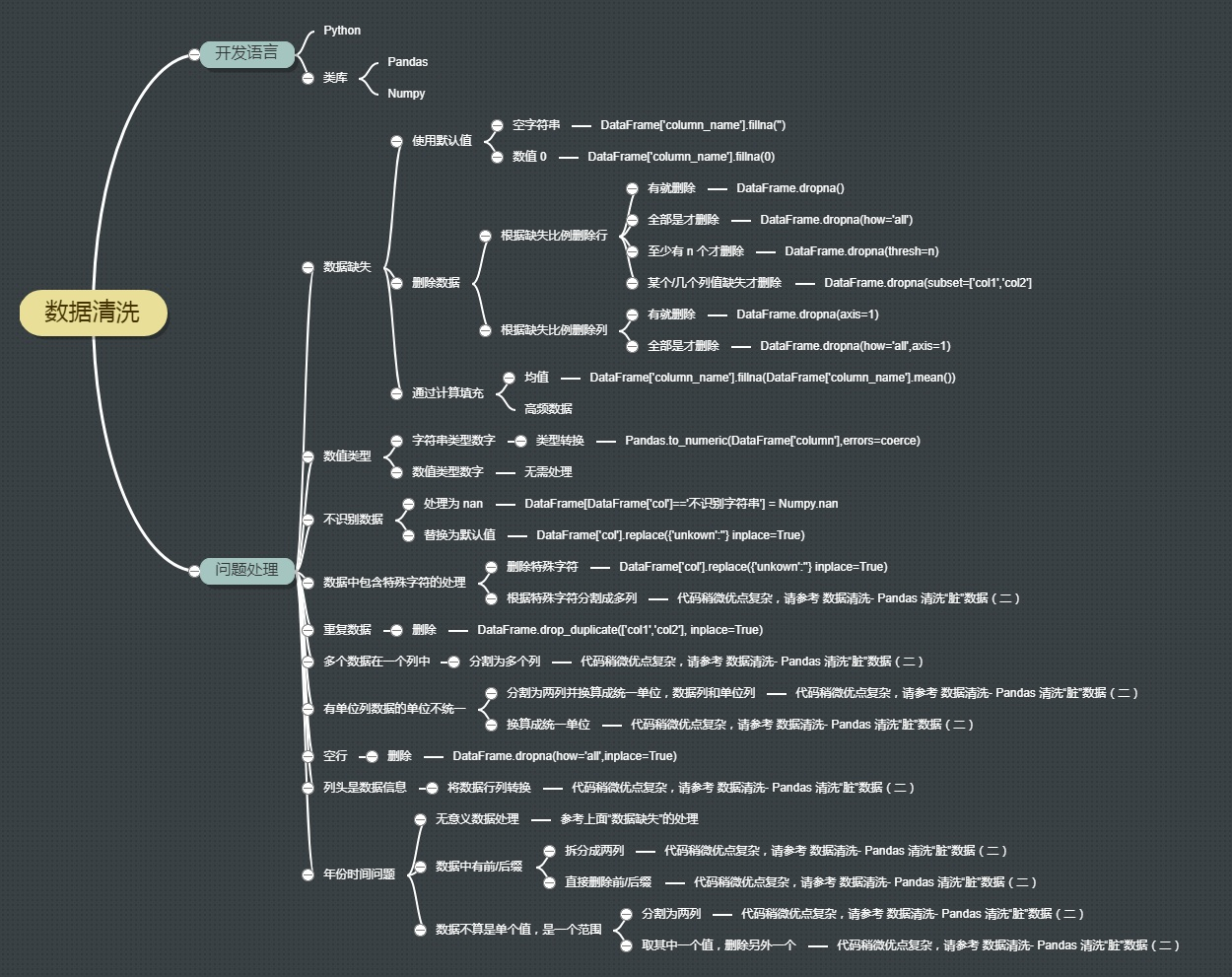
知乎专栏:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/dataclean
参考网址:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/20571505
pandas 小知识点学习参考
https://blog.csdn.net/tanzuozhev/column/info/16726
- 数据表中的重复值duplicated() & drop_duplicates()
- 数据表中的空值 isnull() & notnull() & fillna(0)–>填充nan为0 & dropna()
- 数据间的空格
loandata['term']=loandata['term'].map(str.strip) loandata['term']=loandata['term'].map(str.lstrip) loandata['term']=loandata['term'].map(str.rstrip) - 大小写转换:
loandata['term']=loandata['term'].map(str.upper) loandata['term']=loandata['term'].map(str.lower) loandata['term']=loandata['term'].map(str.title)
数据清洗
- pandas中Dataframe的查询方法([], loc, iloc, at, iat, ix):https://blog.csdn.net/wr339988/article/details/65446138
- pandas学习笔记5—DataFrame数据筛选loc,iloc,ix,at,iat:https://blog.csdn.net/liuweiyuxiang/article/details/78241530
- https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000014117720
- 索引修改
- 正则清洗数据
- 删除 DataFrame 中的不必要 columns
- 改变 DataFrame 的 index
- 使用 .str() 方法来清洗 columns
- 使用 DataFrame.applymap() 函数按元素的清洗整个数据集
- 重命名 columns 为一组更易识别的标签
- 滤除 CSV文件中不必要的 rows
- loc基于索引、iloc基于位置
Pandas透视表(pivot_table)详解
https://blog.csdn.net/liuweiyuxiang/article/details/78183896
inplace=True–>表示在原数据或者结构上进行操作修改
pandas的factorize()理解
factorize函数可以将Series中的标称型数据映射称为一组数字,相同的标称型映射为相同的数字。factorize函数的返回值是一个tuple(元组),元组中包含两个元素。第一个元素是一个array,其中的元素是标称型元素映射为的数字;第二个元素是Index类型,其中的元素是所有标称型元素,没有重复。
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
In [43]: df = pd.DataFrame({"id":[1,2,3,4,5,6,3,2], "raw_grade":['a', 'b', 'b',
...: 'a', 'a', 'e','c','a']})
In [44]: df
Out[44]:
id raw_grade
0 1 a
1 2 b
2 3 b
3 4 a
4 5 a
5 6 e
6 3 c
7 2 a
In [45]: x = pd.factorize(df.raw_grade)
In [46]: x
Out[46]:
(array([0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 3, 0], dtype=int64),
Index(['a', 'b', 'e', 'c'], dtype='object'))
#array中的元素其实是df.raw_grade的对应位置元素在Index中的下标。例如array第一个元素是0,表示df.raw_grade的第一个元素为Index的第0个元素。
In [47]: x[1]
Out[47]: Index(['a', 'b', 'e', 'c'], dtype='object')
In [48]: x[0]
Out[48]: array([0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 3, 0], dtype=int64)
In [49]: type(x)
Out[49]: tuple
pandas 修改DataFrame列名
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/liuweiyuxiang/article/details/78445440
>>>a.rename(columns={'A':'a', 'B':'b', 'C':'c'}, inplace = True)
>>>a
a b c
0 1 4 7
1 2 5 8
2 3 6 9
>>>a.rename(columns={'A':'a', 'C':'c'}, inplace = True) # inplace的意思是在原DataFrame上完成
>>>a
a B c
0 1 4 7
1 2 5 8
2 3 6 9
# 可以只修改A,C两列的名称,而不修改B。
pandas 值的替换
replace_map={
-999:None
}
obj.replace(replace_map)
||
frame.rename(
index={'Ohio':'Indiana'},
columns={'three':'peekaboo'},
inplace=True
)
数据重排与随机采样
根据给定的索引对行进行重排,选取数据等。
frame=pd.DataFrame(np.arange(20).reshape((5,4)))
re_order=np.random.permutation(frame.shape[0])
training_set=frame.iloc[re_order[:3],:]
test_set=frame.iloc[re_order[3:],:]
mini_batch=training_set.sample(1,replace=True)
非 ASCII 字符
# 删除非 ASCII 字符
df['first_name'].replace({r'[^\x00-\x7F]+':''}, regex=True, inplace=True)
df['last_name'].replace({r'[^\x00-\x7F]+':''}, regex=True, inplace=True)
pandas中关于axis的理解
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/liuweiyuxiang/article/details/80895844
例如一个shape(3,2,4)的数组,代表一个三维数组,要注意的是这里的维度与物理学的维度的理解是不太一样的 axis = 0时,就相当于所求的数组的结果变成shape(2,4) axis = 1时,数组的结果shape(3,4) axis = 2时,数组的结果shape(3,2) 这里应该看出来了,当axis=n的时候shape中相应的索引就会被去除,数组发生了降维,那么是如何降维的呢?首先要清楚shape里的数字都代表什么意义: 3代表这个numpy数组里嵌套着3个数组(有三层), 2代表其中每个数组的行数,3代表其中每个数组的列数。
>>>df = pd.DataFrame([[1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3, 3]], \
columns=["col1", "col2", "col3", "col4"])
>>>df
col1 col2 col3 col4
0 1 1 1 1
1 2 2 2 2
2 3 3 3 3
# 如果我们调用df.mean(axis=1),我们将得到按行计算的均值
>>> df.mean(axis=1)
0 1
1 2
2 3
然而,如果我们调用 df.drop((name, axis=1),我们实际上删掉了一列,而不是一行:
>>> df.drop("col4", axis=1)
col1 col2 col3
0 1 1 1
1 2 2 2
2 3 3 3
其实问题理解axis有问题,df.mean其实是在每一行上取所有列的均值,而不是保留每一列的均值。也许简单的来记就是axis=0代表往跨行(down),而axis=1代表跨列(across),作为方法动作的副词(译者注)
换句话说:
- 使用0值表示沿着每一列或行标签\索引值向下执行方法
- 使用1值表示沿着每一行或者列标签模向执行对应的方法
下图代表在DataFrame当中axis为0和1时分别代表的含义:
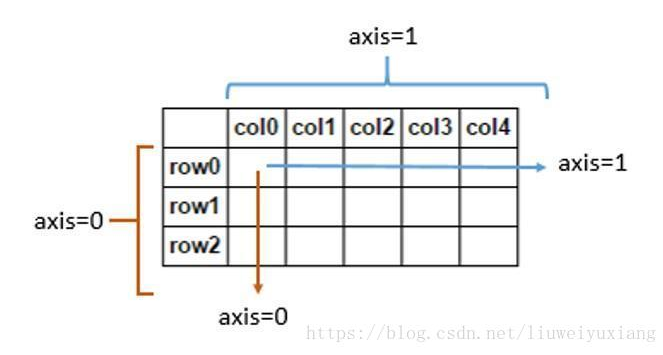
axis参数作用方向图示。另外,记住,Pandas保持了Numpy对关键字axis的用法,用法在Numpy库的词汇表当中有过解释:轴用来为超过一维的数组定义的属性,二维数据拥有两个轴:第0轴沿着行的垂直往下,第1轴沿着列的方向水平延伸。 所以问题当中第一个列子 df.mean(axis=1)代表沿着列水平方向计算均值,而第二个列子df.drop(name, axis=1) 代表将name对应的列标签(们)沿着水平的方向依次删掉。即df.mean(axis=1)表示一行一行的计算均值,df.drop(name, axis=1)表示一行一行的将name列删掉。还可以这样理解,axis等于那个维度代表操作在哪个维度上进行,操作后该维度消失(变成1)。如df.mean(axis=1),axis=1表示均值操作在列上进行(跨列操作),即按照行相加求均值,操作后变成一列。axis指定哪个维度表示跨哪个维度进行操作。
scikit-learn中评估分类器性能的度量,像混淆矩阵、ROC、AUC等
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/liuweiyuxiang/article/details/78475419
数据处理常用函数大全
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pandas import read_csv;
from pandas import to_datetime;
---------------numpy-----------------------
arr = np.array([1,2,3], dtype=np.float64)
np.zeros((3,6)) np.empty((2,3,2)) np.arange(15)
arr.dtype arr.ndim arr.shape
arr.astype(np.int32) #np.float64 np.string_ np.unicode_
arr * arr arr - arr 1/arr
arr= np.arange(32).reshape((8,4))
arr[1:3, : ] #正常切片
arr[[1,2,3]] #花式索引
arr.T arr.transpose((...)) arr.swapaxes(...) #转置
arr.dot #矩阵内积
np.sqrt(arr) np.exp(arr) randn(8)#正态分布值 np.maximum(x,y)
np.where(cond, xarr, yarr) #当cond为真,取xarr,否则取yarr
arr.mean() arr.mean(axis=1) #算术平均数
arr.sum() arr.std() arr.var() #和、标准差、方差
arr.min() arr.max() #最小值、最大值
arr.argmin() arr.argmax() #最小索引、最大索引
arr.cumsum() arr.cumprod() #所有元素的累计和、累计积
arr.all() arr.any() # 检查数组中是否全为真、部分为真
arr.sort() arr.sort(1) #排序、1轴向上排序
arr.unique() #去重
np.in1d(arr1, arr2) #arr1的值是否在arr2中
np.load() np.loadtxt() np.save() np.savez() #读取、保存文件
np.concatenate([arr, arr], axis=1) #连接两个arr,按行的方向
---------------pandas-----------------------
ser = Series() ser = Series([...], index=[...]) #一维数组, 字典可以直接转化为series
ser.values ser.index ser.reindex([...], fill_value=0) #数组的值、数组的索引、重新定义索引
ser.isnull() pd.isnull(ser) pd.notnull(ser) #检测缺失数据
ser.name= ser.index.name= #ser本身的名字、ser索引的名字
ser.drop('x') #丢弃索引x对应的值
ser +ser #算术运算
ser.sort_index() ser.order() #按索引排序、按值排序
df = DataFrame(data, columns=[...], index=[...]) #表结构的数据结构,既有行索引又有列索引
df.ix['x'] #索引为x的值 对于series,直接使用ser['x']
del df['ly'] #用del删除第ly列
df.T #转置
df.index.name df.columns.name df.values
df.drop([...])
df + df df1.add(df2, fill_vaule=0) #算术运算
df -ser #df与ser的算术运算
f=lambda x: x.max()-x.min() df.apply(f)
df.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False) #按行索引排序
df.sort_index(by=['a','b']) #按a、b列索引排序
ser.rank() df.rank(axis=1) #排序,增设一个排名值
df.sum() df.sum(axis=1) #按列、按行求和
df.mean(axis=1, skipna=False) #求各行的平均值,考虑na的存在
df.idxmax() #返回最大值的索引
df.cumsum() #累计求和
df.describe() ser.describe() #返回count mean std min max等值
ser.unique() #去重
ser.value_counts() df.value_counts() #返回一个series,其索引为唯一值,值为频率
ser.isin(['x', 'y']) #判断ser的值是否为x,y,得到布尔值
ser.dropna() ser.isnull() ser.notnull() ser.fillna(0) #处理缺失数据,df相同
df.unstack() #行列索引和值互换 df.unstack().stack()
df.swaplevel('key1','key2') #接受两个级别编号或名称,并互换
df.sortlevel(1) #根据级别1进行排序,df的行、列索引可以有两级
df.set_index(['c','d'], drop=False) #将c、d两列转换为行,因drop为false,在列中仍保留c,d
read_csv read_table read_fwf #读取文件分隔符为逗号、分隔符为制表符('\t')、无分隔符(固定列宽)
pd.read_csv('...', nrows=5) #读取文件前5行
pd.read_csv('...', chunksize=1000) #按块读取,避免过大的文件占用内存
pd.load() #pd也有load方法,用来读取二进制文件
pd.ExcelFile('...xls').parse('Sheet1') # 读取excel文件中的sheet1
df.to_csv('...csv', sep='|', index=False, header=False) #将数据写入csv文件,以|为分隔符,默认以,为分隔符, 禁用列、行的标签
pd.merge(df1, df2, on='key', suffixes=('_left', '_right')) #合并两个数据集,类似数据库的inner join, 以二者共有的key列作为键,suffixes将两个key分别命名为key_left、key_right
pd.merge(df1, df2, left_on='lkey', right_on='rkey') #合并,类似数据库的inner join, 但二者没有同样的列名,分别指出,作为合并的参照
pd.merge(df1, df2, how='outer') #合并,但是是outer join;how='left'是笛卡尔积,how='inner'是...;还可以对多个键进行合并
df1.join(df2, on='key', how='outer') #也是合并
pd.concat([ser1, ser2, ser3], axis=1) #连接三个序列,按行的方向
ser1.combine_first(ser2) df1.combine_first(df2) #把2合并到1上,并对齐
df.stack() df.unstack() #列旋转为行、行旋转为列
df.pivot()
df.duplicated() df.drop_duplicates() #判断是否为重复数据、删除重复数据
df[''].map(lambda x: abs(x)) #将函数映射到df的指定列
ser.replace(-999, np.nan) #将-999全部替换为nan
df.rename(index={}, columns={}, inplace=True) #修改索引,inplace为真表示就地修改数据集
pd.cut(ser, bins) #根据面元bin判断ser的各个数据属于哪一个区段,有labels、levels属性
df[(np.abs(df)>3).any(1)] #输出含有“超过3或-3的值”的行
permutation take #用来进行随机重排序
pd.get_dummies(df['key'], prefix='key') #给df的所有列索引加前缀key
df[...].str.contains() df[...].str.findall(pattern, flags=re.IGNORECASE) df[...].str.match(pattern, flags=...) df[...].str.get() #矢量化的字符串函数
----绘图
ser.plot() df.plot() #pandas的绘图工具,有参数label, ax, style, alpha, kind, logy, use_index, rot, xticks, xlim, grid等,详见page257
kind='kde' #密度图
kind='bar' kind='barh' #垂直柱状图、水平柱状图,stacked=True为堆积图
ser.hist(bins=50) #直方图
plt.scatter(x,y) #绘制x,y组成的散点图
pd.scatter_matrix(df, diagonal='kde', color='k', alpha='0.3') #将df各列分别组合绘制散点图
----聚合分组
groupby() 默认在axis=0轴上分组,也可以在1组上分组;可以用for进行分组迭代
df.groupby(df['key1']) #根据key1对df进行分组
df['key2'].groupby(df['key1']) #根据key1对key2列进行分组
df['key3'].groupby(df['key1'], df['key2']) #先根据key1、再根据key2对key3列进行分组
df['key2'].groupby(df['key1']).size() #size()返回一个含有分组大小的series
df.groupby(df['key1'])['data1'] 等价于 df['data1'].groupby(df['key1'])
df.groupby(df['key1'])[['data1']] 等价于 df[['data1']].groupby(df['key1'])
df.groupby(mapping, axis=1) ser(mapping) #定义mapping字典,根据字典的分组来进行分组
df.groupby(len) #通过函数来进行分组,如根据len函数
df.groupby(level='...', axis=1) #根据索引级别来分组
df.groupby([], as_index=False) #禁用索引,返回无索引形式的数据
df.groupby(...).agg(['mean', 'std']) #一次使用多个聚合函数时,用agg方法
df.groupby(...).transform(np.mean) #transform()可以将其内的函数用于各个分组
df.groupby().apply() #apply方法会将待处理的对象拆分成多个片段,然后对各片段调用传入的函数,最后尝试将各片段组合到一起
----透视交叉
df.pivot_table(['',''], rows=['',''], cols='', margins=True) #margins为真时会加一列all
pd.crosstab(df.col1, df.col2, margins=True) #margins作用同上
---------------matplotlib---------------
fig=plt.figure() #图像所在的基对象
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,2,1) #2*2的图像,当前选中第1个
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows, nclos, sharex, sharey) #创建图像,指定行、列、共享x轴刻度、共享y轴刻度
plt.subplots_adjust(left=None, bottom=None, right=None, top=None, wspace=None, hspace=None)
#调整subplot之间的距离,wspace、hspace用来控制宽度、高度百分比
ax.plot(x, y, linestyle='--', color='g') #依据x,y坐标画图,设置线型、颜色
ax.set_xticks([...]) ax.set_xticklabels([...]) #设置x轴刻度
ax.set_xlabel('...') #设置x轴名称
ax.set_title('....') #设置图名
ax.legend(loc='best') #设置图例, loc指定将图例放在合适的位置
ax.text(x,y, 'hello', family='monospace', fontsize=10) #将注释hello放在x,y处,字体大小为10
ax.add_patch() #在图中添加块
plt.savefig('...png', dpi=400, bbox_inches='tight') #保存图片,dpi为分辨率,bbox=tight表示将裁减空白部分
------------------------------------------
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#可以用来绘制地图
-----------------时间序列--------------------------
pd.to_datetime(datestrs) #将字符串型日期解析为日期格式
pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=1000) #生成时间序列
ts.resample('D', how='mean') #采样,将时间序列转换成以每天为固定频率的, 并计算均值;how='ohlc'是股票四个指数;
#重采样会聚合,即将短频率(日)变成长频率(月),对应的值叠加;
#升采样会插值,即将长频率变为短频率,中间产生新值
ts.shift(2, freq='D') ts.shift(-2, freq='D') #后移、前移2天
now+Day() now+MonthEnd()
import pytz pytz.timezone('US/Eastern') #时区操作,需要安装pytz
pd.Period('2010', freq='A-DEC') #period表示时间区间,叫做时期
pd.PeriodIndex #时期索引
ts.to_period('M') #时间转换为时期
pd.rolling_mean(...) pd.rolling_std(...) #移动窗口函数-平均值、标准差
df = read_csv('D:\\PA\\4.18\\data.csv', encoding='utf8')
df_dt = to_datetime(df.注册时间, format='%Y/%m/%d');
df_dt.dt.year
df_dt.dt.second;
df_dt.dt.minute;
df_dt.dt.hour;
df_dt.dt.day;
df_dt.dt.month;
df_dt.dt.weekday;
处理丢失数据
df.dropna(
axis=0, # 0: 对行进行操作; 1: 对列进行操作
how='any' # 'any': 只要存在 NaN 就 drop 掉; 'all': 必须全部是 NaN 才 drop
)
df.fillna(value=0)
df.isnull() # 得到的是布尔型的矩阵
np.any(df.isnull()) == True # 判断是否存在Nan
导入导出数据
import pandas as pd #加载模块
#读取csv
data = pd.read_csv('student.csv')
#打印出data
print(data)
data.to_pickle('student.pickle') # 将资料存取成pickle





