gcc的编译关于程序保护开启的选项
- CANNARY(栈保护)
gcc -o test test.c // 默认情况下,不开启Canary保护 gcc -fno-stack-protector -o test test.c //禁用栈保护 gcc -fstack-protector -o test test.c //启用堆栈保护,不过只为局部变量中含有 char 数组的函数插入保护代码 gcc -fstack-protector-all -o test test.c //启用堆栈保护,为所有函数插入保护代码 - NX(DEP)
NX即No-eXecute(不可执行)的意思,NX(DEP)的基本原理是将数据所在内存页标识为不可执行,当程序溢出成功转入shellcode时,程序会尝试在数据页面上执行指令,此时CPU就会抛出异常,而不是去执行恶意指令。
工作原理如图:
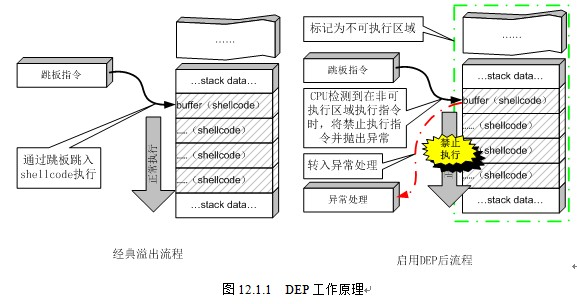
gcc编译器默认开启了NX选项,如果需要关闭NX选项,可以给gcc编译器添加-z execstack参数。
gcc -o test test.c // 默认情况下,开启NX保护
gcc -z execstack -o test test.c // 禁用NX保护
gcc -z noexecstack -o test test.c // 开启NX保护
- PIE(ASLR)
一般情况下NX(Windows平台上称其为DEP)和地址空间分布随机化(ASLR)会同时工作。 内存地址随机化机制(address space layout randomization),有以下三种情况
0 - 表示关闭进程地址空间随机化。
1 - 表示将mmap的基址,stack和vdso页面随机化。
2 - 表示在1的基础上增加栈(heap)的随机化。
可以防范基于Ret2libc方式的针对DEP的攻击。ASLR和DEP配合使用,能有效阻止攻击者在堆栈上运行恶意代码。
Built as PIE:位置独立的可执行区域(position-independent executables)。这样使得在利用缓冲溢出和移动操作系统中存在的其他内存崩溃缺陷时采用面向返回的编程(return-oriented programming)方法变得难得多。
liunx下关闭PIE的命令如下:
sudo -s echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
gcc -o test test.c // 默认情况下,开启PIE保护
gcc -no-pie -o test test.c // 禁用PIE保护
- RELRO
在Linux系统安全领域数据可以写的存储区就会是攻击的目标,尤其是存储函数指针的区域。 所以在安全防护的角度来说尽量减少可写的存储区域对安全会有极大的好处.
GCC, GNU linker以及Glibc-dynamic linker一起配合实现了一种叫做relro的技术: read only relocation。大概实现就是由linker指定binary的一块经过dynamic linker处理过 relocation之后的区域为只读.
设置符号重定向表格为只读或在程序启动时就解析并绑定所有动态符号,从而减少对GOT(Global Offset Table)攻击。RELRO为” Partial RELRO”,说明我们对GOT表具有写权限。
gcc -o test test.c // 默认情况下,是Partial RELRO
gcc -z norelro -o test test.c // 关闭,即No RELRO
gcc -z lazy -o test test.c // 部分开启,即Partial RELRO
gcc -z now -o test test.c // 全部开启,即
- 总结
NX:-z execstack / -z noexecstack (关闭 / 开启) Canary:-fno-stack-protector /-fstack-protector / -fstack-protector-all (关闭 / 开启 / 全开启) PIE:-no-pie / -pie (关闭 / 开启) RELRO:-z norelro / -z lazy / -z now (关闭 / 部分开启 / 完全开启)
附上gcc的命令说明
Usage: gcc [options] file...
Options:
-pass-exit-codes Exit with highest error code from a phase.
--help Display this information.
--target-help Display target specific command line options.
--help={common|optimizers|params|target|warnings|[^]{joined|separate|undocumented}}[,...].
Display specific types of command line options.
(Use '-v --help' to display command line options of sub-processes).
--version Display compiler version information.
-dumpspecs Display all of the built in spec strings.
-dumpversion Display the version of the compiler.
-dumpmachine Display the compiler's target processor.
-print-search-dirs Display the directories in the compiler's search path.
-print-libgcc-file-name Display the name of the compiler's companion library.
-print-file-name=<lib> Display the full path to library <lib>.
-print-prog-name=<prog> Display the full path to compiler component <prog>.
-print-multiarch Display the target's normalized GNU triplet, used as
a component in the library path.
-print-multi-directory Display the root directory for versions of libgcc.
-print-multi-lib Display the mapping between command line options and
multiple library search directories.
-print-multi-os-directory Display the relative path to OS libraries.
-print-sysroot Display the target libraries directory.
-print-sysroot-headers-suffix Display the sysroot suffix used to find headers.
-Wa,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the assembler.
-Wp,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the preprocessor.
-Wl,<options> Pass comma-separated <options> on to the linker.
-Xassembler <arg> Pass <arg> on to the assembler.
-Xpreprocessor <arg> Pass <arg> on to the preprocessor.
-Xlinker <arg> Pass <arg> on to the linker.
-save-temps Do not delete intermediate files.
-save-temps=<arg> Do not delete intermediate files.
-no-canonical-prefixes Do not canonicalize paths when building relative
prefixes to other gcc components.
-pipe Use pipes rather than intermediate files.
-time Time the execution of each subprocess.
-specs=<file> Override built-in specs with the contents of <file>.
-std=<standard> Assume that the input sources are for <standard>.
--sysroot=<directory> Use <directory> as the root directory for headers
and libraries.
-B <directory> Add <directory> to the compiler's search paths.
-v Display the programs invoked by the compiler.
-### Like -v but options quoted and commands not executed.
-E Preprocess only; do not compile, assemble or link.
-S Compile only; do not assemble or link.
-c Compile and assemble, but do not link.
-o <file> Place the output into <file>.
-pie Create a position independent executable.
-shared Create a shared library.
-x <language> Specify the language of the following input files.
Permissible languages include: c c++ assembler none
'none' means revert to the default behavior of
guessing the language based on the file's extension.
Options starting with -g, -f, -m, -O, -W, or --param are automatically
passed on to the various sub-processes invoked by gcc. In order to pass
other options on to these processes the -W<letter> options must be used.
For bug reporting instructions, please see:
<file:///usr/share/doc/gcc-7/README.Bugs>.





